How the brain sees the world around us and interprets it to serve you is fascinating, to say the very least. Without our complex brains, we would see many objects differently. In this post, we will talk about parallel processing psychology. What is it? How does it affect how we observe the life around us? Why does it matter?
Table of Contents
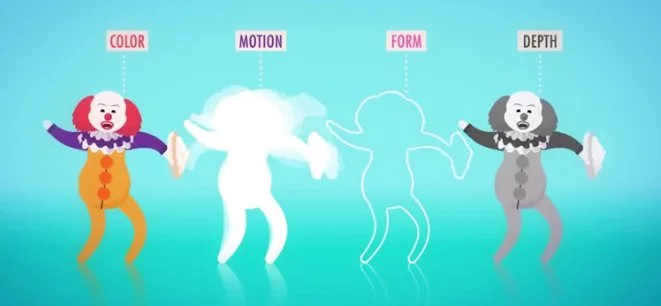
What is parallel processing psychology?
Parallel processing psychology is basically, the capacity of the mind to perform many jobs at the same time. As an instance, when you see an item, your mind makes observations regarding its color, shape, texture, and dimensions to recognize that thing correctly. Observing these distinct traits requires your mind to do several tasks at the same time.
Another parallel processing definition of psychology must do with how different systems interact together. Government institutions, associations, counselors, and customers all exist within systems which are nested within one another. Whatever impacts these systems affects all of these. Consequently, if a counselor is influenced by dysfunction within society, then they may bring a number of that dysfunction together to the counselling relationship.
Another sort of “parallel processing” may happen in reaction to this particular malfunction. If you’re a customer, then you might not even be aware it is occurring because it occurs outside the treatment session. The therapist takes the customer’s function, and their manager takes on the part of the therapist.
By way of instance, a therapist might realize they have already been “stuck” during the past couple of sessions with a customer. They continue over and above precisely the exact same battle, emotions, or scenario without getting everywhere, and the two parties start to feel frustrated. There are various reasons this might be occurring (which we will touch on later), but in this specific scenario, the counselor might require some assistance from a manager. Since the counselor assumes the part of their customer and encounters their manager’s answer to the circumstance they develop new insights concerning the situation that may help them handle their customer more efficiently.
How does parallel processing in psychology works?
The potency of parallel processing psychology is determined by two processes: transference, and countertransference. Both procedures are unconscious, but comprehension of these is vital for the treatment to work.
Transference
In transference, the adviser describes their customer and automatically reflects the customer’s behaviors and thought processes during parallel processing. There are a myriad of reasons that this could be occurring. From time to time, the counselor is only hoping to place themselves in the customer’s shoes to empathize much better. Additionally, it is possible that the counselor or therapist might be fighting with a few of the very same problems that their customer is coping with. In the end, many therapists enter the profession because they see treatment as a path to recovery. Subsequently, the supervisor models answers or potential answers.
CounterTransference
For quite a while, it had been believed that parallel processing has been occurring in 1 direction only, together with transference the only method whereby a solution could occur. But after research has discovered that the consequences of parallel processing proceed in a different direction too: by the supervisor back to the customer through the practice of countertransference.
The therapist replicate the counselling scenario, but the association between the therapist and their supervisor is reflected back to the customer, since the therapist unconsciously describes their supervisor and passes across the very same answers to the customer.
Benefits of parallel processing psychology?
- Parallel processing may hasten the client-counselor procedure. If it looks like exactly the very same events are revisited over and over again, parallel processing can help find a new view and get out of this hole that’s repeating the very same events.
- Parallel processing can aid a counselor outside also. Counselors aren’t robots, and they suffer from their own. When there’s a conflict between client and counsel, parallel processing operates by finding the main reason behind the battle and enabling the two to solve.
- Parallel processing will help to allow for manifestation. A counselor should look in their advancement in a reflective way.
- Finally, parallel processing might help counselors de-stress You might believe a counselor is desensitized with of the strain, but you’re incorrect. Rather, mental health advisor is among the most stressful tasks on the market. Someone is constantly exposed to the annoyance of the others, and a particularly empathetic counselor can internalize all of the pain and let it fester, which is not good.
Disadvantages of parallel processing psychology
Here are some potential downsides to this parallel processing System:
- Lack of consciousness. The transference and countertransference procedures can occur with no therapist or the supervisor being mindful of these. With this self-awareness, therapy may stay stuck in the exact same unproductive pattern. It requires specific manifestation on problems as they appear to break those patterns and proceed forward.
- The essence of the relationship between the therapist and supervisor could produce the therapist feel defensive and nervous. Contrary to the client-therapist relationship, that can be secure and non invasive, a relationship with a supervisor has the capability to influence a profession for good or ill. As a result of this imbalance of power, therapists could be uneasy simulating a counselling relationship with a supervisor.
- Exhaustion if overused. Parallel processing is very significant if it’s used judiciously, in a context which makes sense. But using it too or using it in the wrong time may make it look superfluous. Any insights obtained could be wholly offset by the utter exhaustion of this strenuous procedure.
YOU CAN ALSO READ ABOUT





1 Comment
great work well done thank you