Organs push through weak areas of the surrounding muscle, causing a hernia. Through the inguinal canal, an inguinal hernia develops in the abdomen.
“These are passages on either side of the groin that run down the lower abdomen. This type of hernia usually manifests itself as a groin bulge,” says Dr. Harsh Sheth, the leading bariatric surgeon from Mumbai.
There are two types of inguinal hernias: direct and indirect. The anatomical location is the difference.
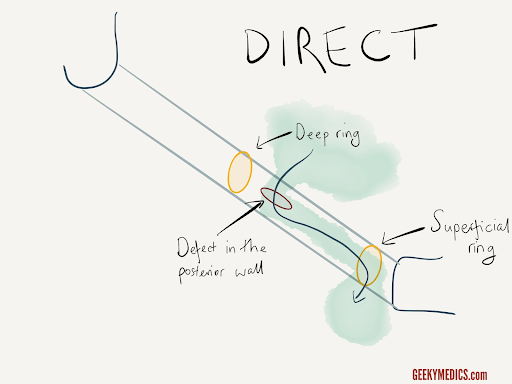
Direct hernias protrude through the inguinal canal’s posterior (back) wall. Hernias that protrude through the inguinal ring are known as indirect hernias.
Direct hernias are caused by heavy lifting or straining, whereas indirect hernias are often congenital.
Learn more about indirect and direct hernias, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Then, to receive the proper treatment, make an appointment with a healthcare professional for a diagnosis.
What are the symptoms, according to Dr. Harsh Sheth
Indirect and direct inguinal hernias are similar in that they both present as bulges in the groin area.
Organs pushing through the inguinal canal cause both of them. Indirect and direct hernias, on the other hand, occur in different places.
Indirect and direct hernias have similar symptoms. They are as follows:
- A groin bulge is a bulge in the groin area.
- A scrotal bulge is a bulge in the scrotum.
- In or around the groin, there may be pain or burning.
Causes
According to Dr. Harsh Sheth, Mumbai’s excellent bariatric surgeon, indirect and direct inguinal hernias have similar symptoms, but the underlying causes are different.
Indirect Inguinal Hernias
They are common in newborns. They are also prevalent in testicular babies.
While one or both from the inguinal canals don’t close throughout fetal growth, this hernia develops.
The failure to completely close the abdomen can cause organs to be pushed outward. Inguinal hernias may be linked to specific genes.
While most indirect inguinal hernias are innate (present at birth), they don’t always manifest themselves in childhood.
As a result, an adult may be diagnosed with an indirect inguinal hernia that did not exist at birth but developed later in life.
This could be due to a weakness in the inguinal ring that has evolved.
Direct Inguinal Hernias
Direct inguinal hernias occur along the inguinal canal’s back wall. They are caused by a weakening of the inguinal canal wall as a person ages.
They are frequently caused by straining or lifting a heavy object.
Direct hernias, like indirect hernias, are more common in people who have testicles.
Only 3% of people with ovaries will develop an inguinal hernia in their lifetime, compared to 27% of people with testicles. This type of hernia is most common in people over the age of 40.
Factors at Risk
Direct inguinal hernias are more common in some people than others. The following are some of the risk factors:
- Disorders of connective tissue (tissues that support and protect other tissues and organs in the body)
- Coughing for a long time
- Constipation that lasts a long time
- Lifting heavy objects
- Standing or walking for extended periods
- Inguinal hernias run in the family
Diagnosis
A physical examination and, in some cases, radiological tests are used to diagnose direct and indirect inguinal hernias.
Your doctor will begin by gathering information about your medical history.
Visually inspecting the area and palpating (touching and pressing) to feel for a hernia are both parts of a physical exam.
Because the hernia may be more visible when standing, you will be asked to stand for the exam.
Your physician will direct you to cough while they check your scrotum if you have testicles.
The doctor will be able to feel the hernia move in and out as a result of this.
If your doctor thinks you need more proof, they may order specific tests. Hernias are diagnosed using the following tests:
- Ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
Treatment
Inguinal hernias do not heal on their own and can become infected.
Inguinal hernias can only be treated surgically, which is why surgery is the only option. Every year, more than 20 million people around the world have groin hernia surgery.
Watchful Waiting
A doctor may use watchful waiting for adults who do not have significant symptoms, closely monitoring but not treating them.
However, it’s important to note that watchful waiting isn’t a substitute for surgery; instead, it’s a delay in receiving surgical repair.
Seventy percent of those who are put off surgery will need it within five years.
In both indirect and direct inguinal hernia surgery, two steps are involved:
- Returning the herniated tissue to its original position
- Repairing the weak spot where the hernia developed (in indirect cases, this consists in closing the inguinal canal)
Your doctor’s recommendation for surgery is based on your age and overall health.
The following are standard surgical procedures:
- Open surgery: To locate and repair the hernia, your doctor will make an incision in your abdomen. When closing the abdominal wall, the surgeon may use stitches and mesh for added support.
- Laparoscopic surgery: This entails making a series of small holes in the abdomen. After that, your doctor will insert special tools to allow the surgeon to see and repair the hernia. This surgery may also include the use of mesh.
A general surgeon or a colorectal surgeon performs both types of surgery under general anesthesia. Inguinal surgery is usually performed as an outpatient procedure, which means you will be able to return home the same day.
Hernia strangulated
Inguinal hernias are rarely caused for concern. On the other hand, a strangulated hernia can result in life-threatening complications because blood flow to trapped tissue is cut off.
Dr.Harsh Sheth from Mumbai suggests critical emergency surgical hernia restoration when strangulation is suspected.
Prevention
It is impossible to prevent indirect inguinal hernias because they are frequently congenital.
However, there are some precautions you can take to reduce your risk of developing a direct inguinal hernia, such as:
- Lift heavy objects carefully.
- When having a bowel movement, don’t strain.
- Constipation should be treated (difficulty moving your bowels).
- Treat a cough that won’t go away.
- If you have to strain to urinate, seek medical help.
- Maintain a healthy weight for yourself.
Summary
Direct inguinal hernias protrude through the inguinal canal’s posterior (back) wall, whereas indirect hernias protrude through the inguinal ring.
Indirect inguinal hernias are frequently congenital, which means they are diagnosed at birth, though not always.
Inguinal hernias of both types are more common in people who have testicles.
A bulge in the groin or scrotum is the most common symptom, and pain may accompany it.
Physical examination is used to make the diagnosis, and imaging may be used to confirm it. After that, surgery is required to correct the issue.
Disclaimer: This article is a paid publication and does not have journalistic/editorial involvement of HealthAndHealthier. HealthAndHealthier does not endorse/subscribe to the content(s) of the article/advertisement and/or view(s) expressed herein. HealthAndHealthier shall not in any manner, be responsible and/or liable in any manner whatsoever for all that is stated in the article and/or also with regard to the view(s), opinion(s), announcement(s), declaration(s), affirmation(s) etc., stated/featured in the same.
Disclaimer